9 Construction Tech Trends to Watch in 2019
- Youtube Views 412,556 VIDEO VIEWS
TECHNOLOGY is impacting the construction industry like never before.
From cloud-based collaboration and the development of digital twins to robots, super-materials, wearable tech, pollution-eating buildings and even artificial intelligence – an incredible array of developments are helping to improve a sector that shapes how every human being on Earth is able to live their lives.
These are the nine construction technology trends to keep your eyes on in 2019.
ROBOTICS
Rapidly moving from science fiction to reality, robots are beginning to enter construction in a number of areas.
From autonomous rovers that can increase the efficiency and detail of site inspections to mechanical arms that automate highly repetitive tasks like brick-laying and tying rebar, the robotic revolution looks set to gather significant pace in 2019.
Above: The B1M's documentary exploring the rise of robotics in construction.
While the credibility of robots on live construction sites has long been questioned, the last 12 months saw a number of real-world trials deliver their results and the unveiling of some astonishing developments.
Now taken seriously, the debate has moved on to how best to integrate robots, the impact they will have on existing job roles and the new skills that will be required as processes become automated.
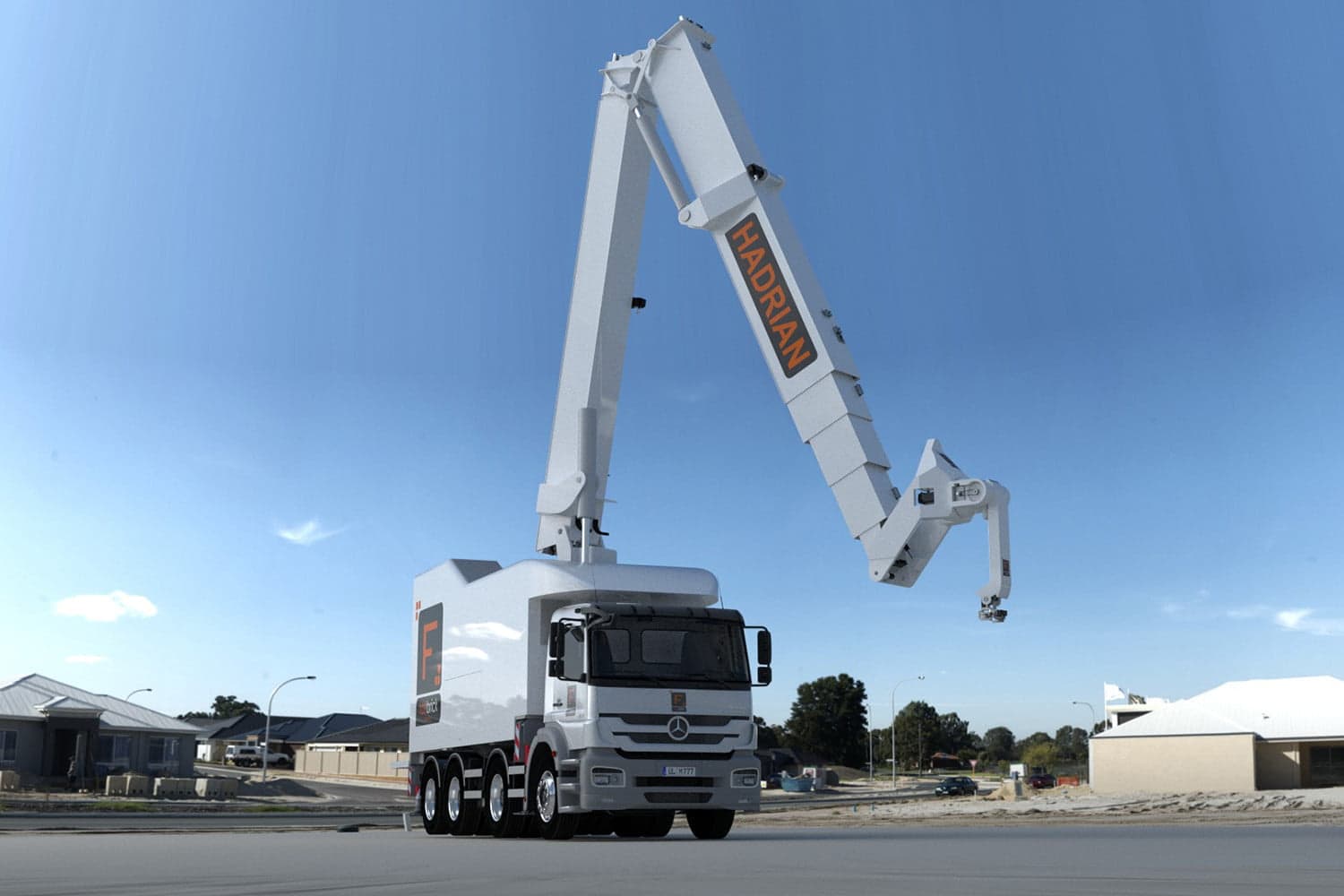

Above: Robots have moved from the lab into real-world trials and the results have been astounding (image courtesy of FBR).
Building on this progress, the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) is also beginning to have an impact on construction.
From the major leaps taken in concepts like predictive design at the project planning stage, to the rise of intelligent buildings that learn how best to operate themselves and serve their users over time, the construction sector will likely find itself at the core of the wider AI debate taking place across our societies in the year ahead.
Though fraught with challenges and inherently disruptive, the rise of automation could give construction the efficiency, productivity and safety breakthroughs it has sought for decades.
EXOSKELETONS
Originally developed for military use and for patient mobility and rehabilitation, exoskeletons are now beginning to appear on construction sites.
Helping to protect workers from manual handling injuries and the risk of hand-arm vibration, these mechanical suits that “augment” with human operatives can also deliver considerable gains in productivity.

Above: An exoskeleton developed by Ekso Bionics (image courtesy of Ekso)
Already being rapidly adopted across manufacturing, live trials on construction sites in the past year have yielded results that look set to drive the development and uptake of exoskeletons in our sector during 2019.
THE CONNECTED JOBSITE
Connected jobsites use cloud technology to make information about almost every aspect of their operation available to all the relevant parties, regardless of whether those parties are on-site or elsewhere.
From putting design information streamed from a single point of truth into the palms of operatives, to information by geolocation, remote site monitoring, personnel location tracking, live mark-ups and the seamless transfer of as-built information – connected job sites improve communication, productivity and safety for everyone involved in a project.
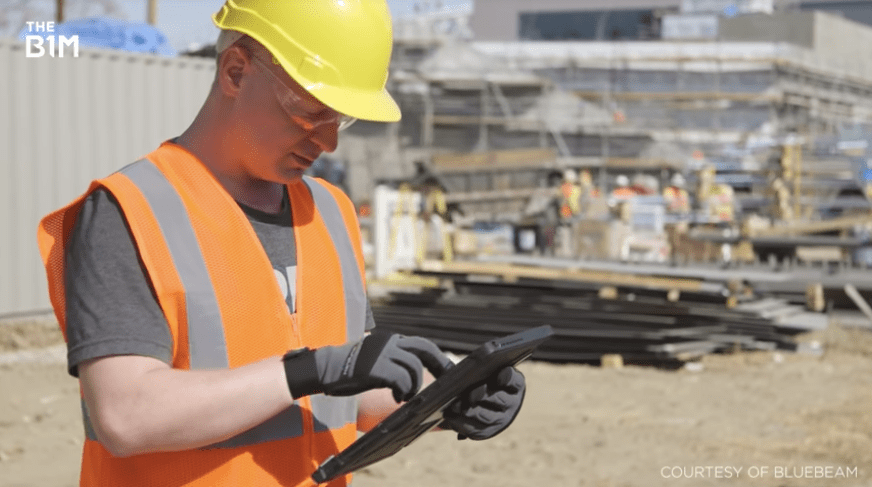

Above and Below: The jobsite is no longer isolated from the rest of the project team (images courtesy of Bluebeam).

With the intuitive technology supporting these sites advancing and now more widely available than ever before, connected job sites are only expected to become more commonplace in 2019.
Meanwhile, developments continue to be made in connecting people and consolidating systems through digital mapping engines that contain and visualize construction data.
New technology like Bluebeam “Atlas” - set to be available in 2019 - is leveraging geospatial mapping to rethink mobile information access.
Mapping design and construction data onto a real-world job site, Atlas uses geo-location to present project information from multiple systems relevant to your physical location, making traditional folder structures obsolete and streamlining any access-critical process like snagging, inspections and more.
AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES
While autonomous vehicles continue to make headlines in the consumer space, their adoption in the construction sector looks set to take notable strides
forward in 2019.
As with the field of robotics, the automation of construction plant – particularly in relation to highly repetitive tasks – could greatly improve productivity, whilst creating a safer work environment and helping to address the industry’s shortfall in labour.

Above: Volvo Construction Equipment's autonomous machines (image courtesy of Volvo Construction Equipment).
At their Electric Site in Sweden, Volvo Construction
Equipment trialled electric autonomous vehicles in conjunction with electric human-operated excavators to deliver a 40% improvement in efficiency
as compared to a traditional set-up.
Other concept vehicles under development by the manufacturer include semi-autonomous electric excavators that can learn the careful movements required to achieve grading or highly accurate levelling.
The combined use of autonomous technology and electric power enables work to take place around the clock without the need for breaks or the disruptive noise levels that traditionally prevent such working.
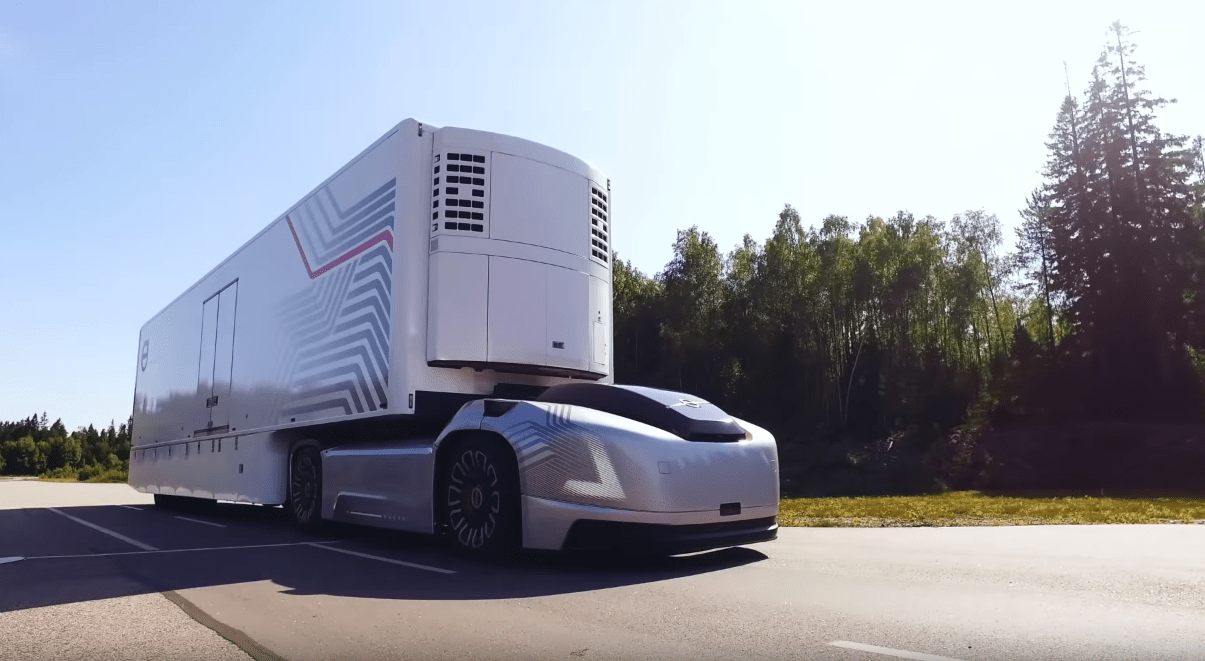
Above: Volvo Trucks have developed a concept fleet of fully autonomous trucks (image courtesy of Volvo Trucks).
Meanwhile, Volvo's Trucks business has made progress in developing a concept fleet of fully autonomous electric vehicles that can help combat pollution, noise and congestion in our cities by reducing emissions, planning optimum routes and responding to real-time traffic situations.
ADVANCED MATERIALS
With growing awareness of the impact that construction has on our environment, technological advances are bringing numerous new material innovations to the fore.
The recycling of hard-to-dispose-of waste products has seen a significant increase, particularly in relation to plastics.
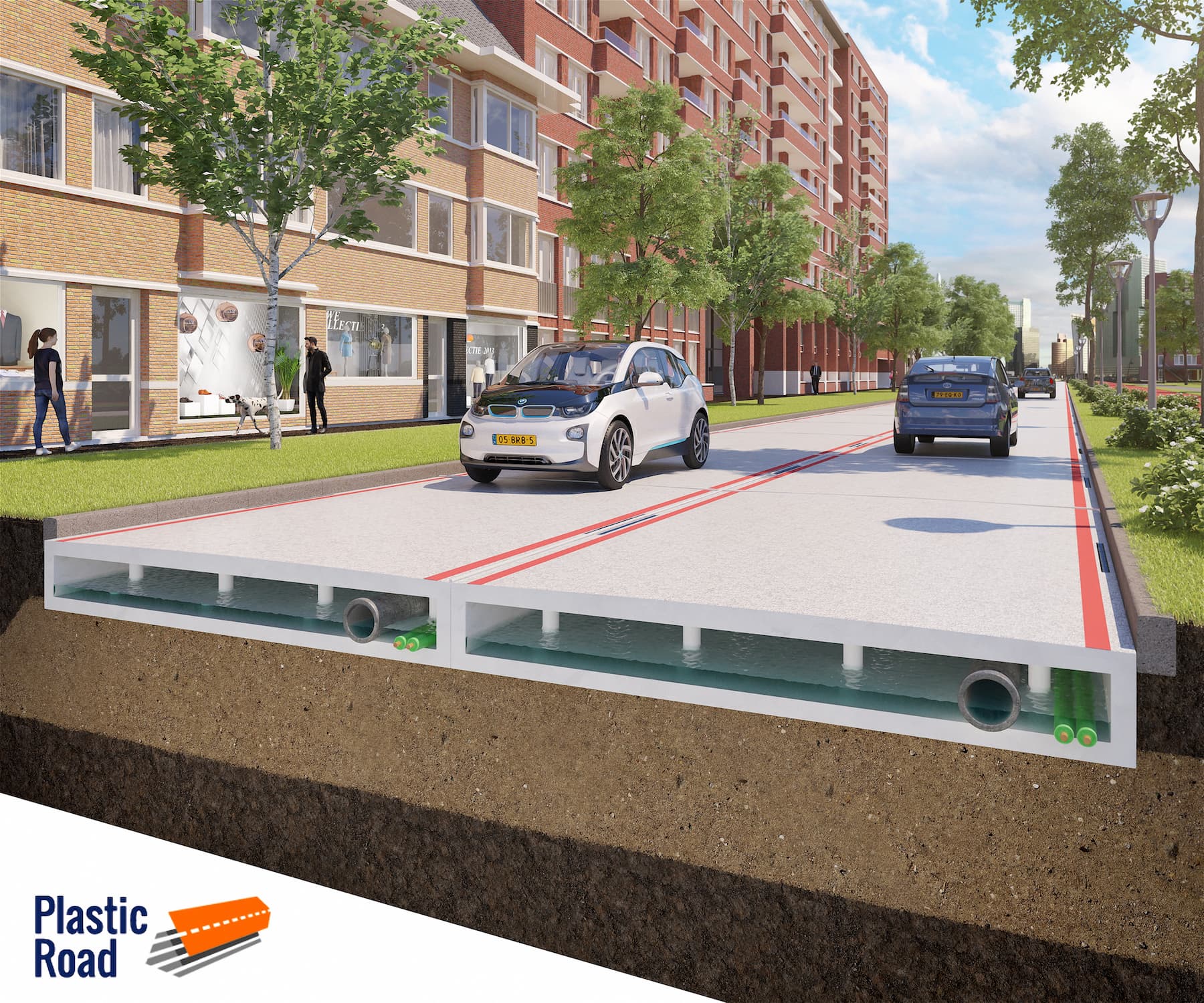

Above: Innovative solutions to our various waste problems, like recycling plastic into roadways, are set to see a significant increase in 2019 ( image courtesy of PlasticRoad).
Recent developments have seen the incorporation of waste plastic into roadways and even its use as a material for 3D printing new building components or structures.
CO2 is another by-product being re-purposed in an effort to reduce the carbon footprint of the industry.
At this project in Atlanta, CO2 was injected into the concrete mix used in the building’s structure.
This carbon dioxide becomes trapped inside the concrete as it cures while chemical reactions within the mix form limestone nanoparticles, that increase the overall compressive strength of the final material.
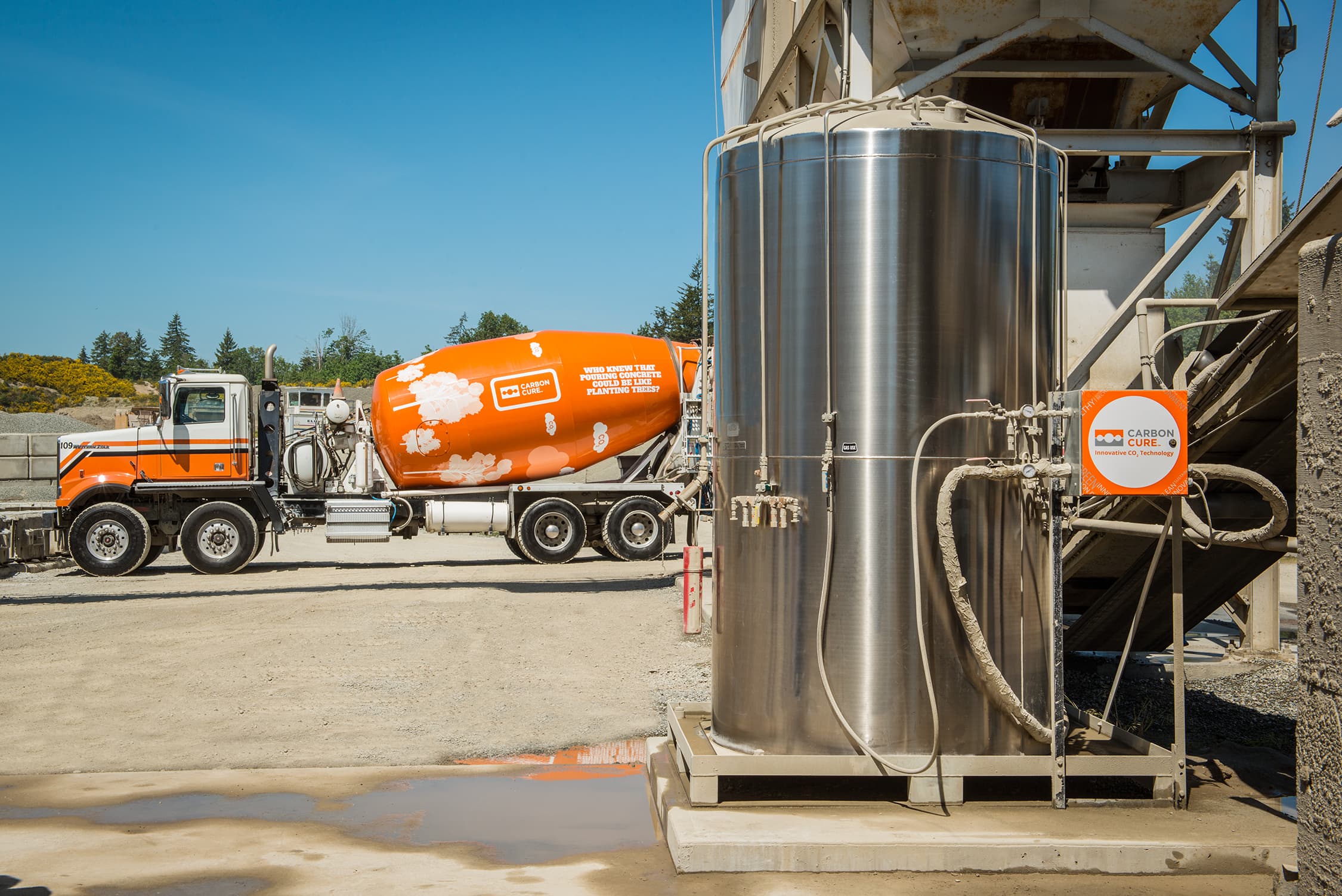

Above: New developments have found ways of using one of our largest waste products to create stronger concrete (image courtesy of CarbonCure).
Staying with one of construction’s most popular materials, "self-healing concrete
Other areas to watch include the continued rise of "kinetic paving" that harvests energy from the footsteps of pedestrians to generate electricity, “4D-printed structures” that have the ability to re-shape or self-assemble over time by virtue of how different elements of their composition respond in differing conditions and “smog-eating buildings” coated in photocatalytic titanium dioxide that reacts with light to neutralise pollutants in the air of some of the world’s most congested cities.
UAVs
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) – also known as “drones” – are set to become increasingly common on construction projects throughout 2019.
From undertaking inspections ensuring that operatives are kept out of harm’s way, to surveying vast areas of land in just a few minutes, the continued rise of UAVs will considerably improve safety and productivity in construction.

Above: UAVs are set to become increasingly common on sites.
In a similar vein to robotics and the rise of automation, debate in this field has matured from one around feasibility to consider the steps needed for a successful implementation – with safety, approvals, privacy, the need for suitable legislation and the urgent demand for specialist skill sets all on the agenda.
VIRTUAL AND AUGMENTED REALITY
While virtual reality (VR) has traditionally enabled project teams and stakeholders to step inside their proposed schemes before construction works commence, the technology is finding countless new applications across the industry as 2019 dawns.
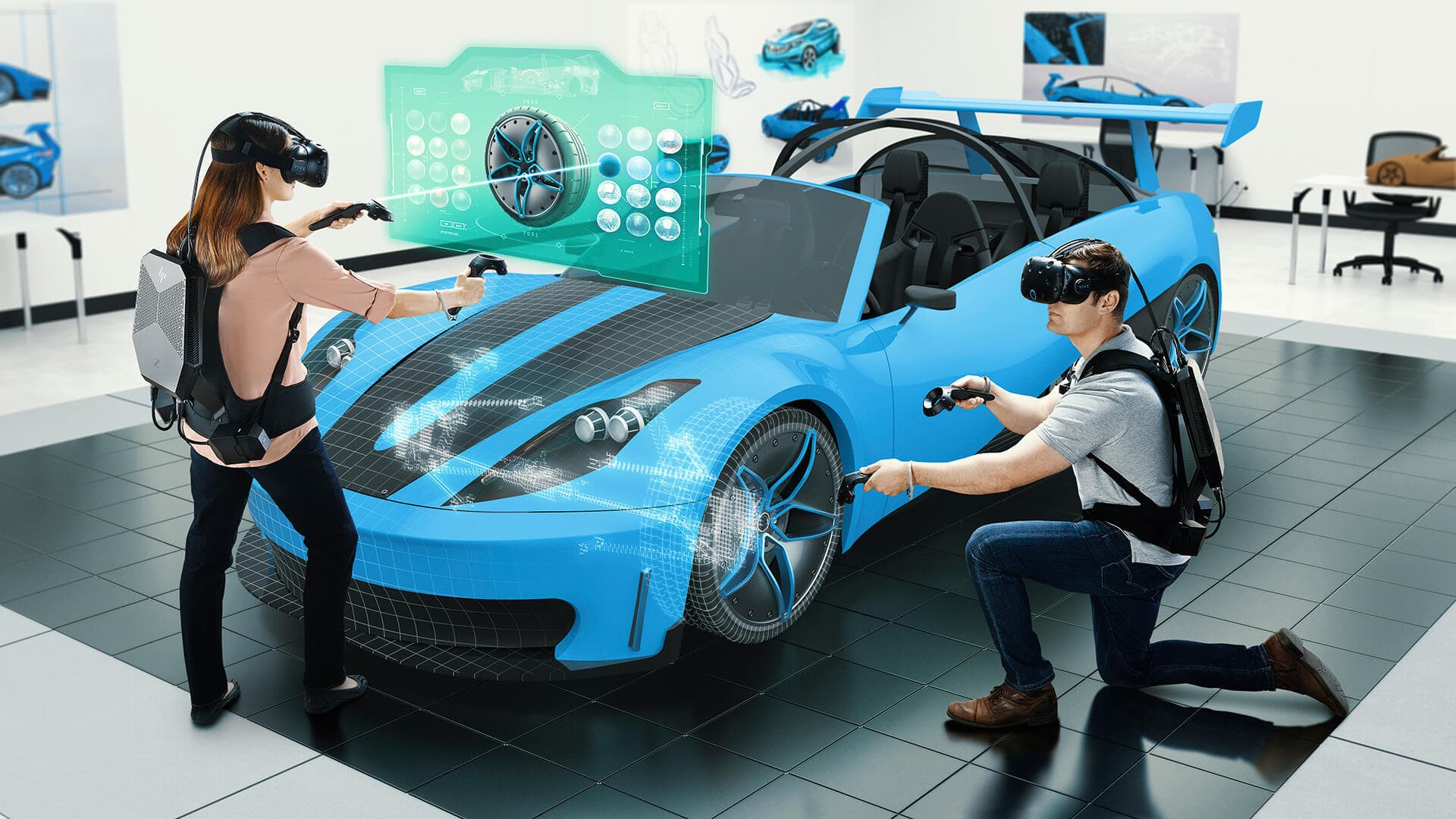

Above: HP have developed a Virtual Reality Backpack PC to create an "untethered" VR experience (image courtesy of Hewlett Packard).
From enabling walk-throughs of complex site logistics plans in advance to supporting health and safety awareness training, VR use has matured in construction and made a largely successful transition from its early days of novelty into a number of practical uses.
In hardware developments, HP’s Virtual Reality Backpack PC allows VR users to enjoy a more realistic “untethered” experience, adding to authenticity and improving outcomes.
Meanwhile, developments continue to be made in augmented reality (AR).
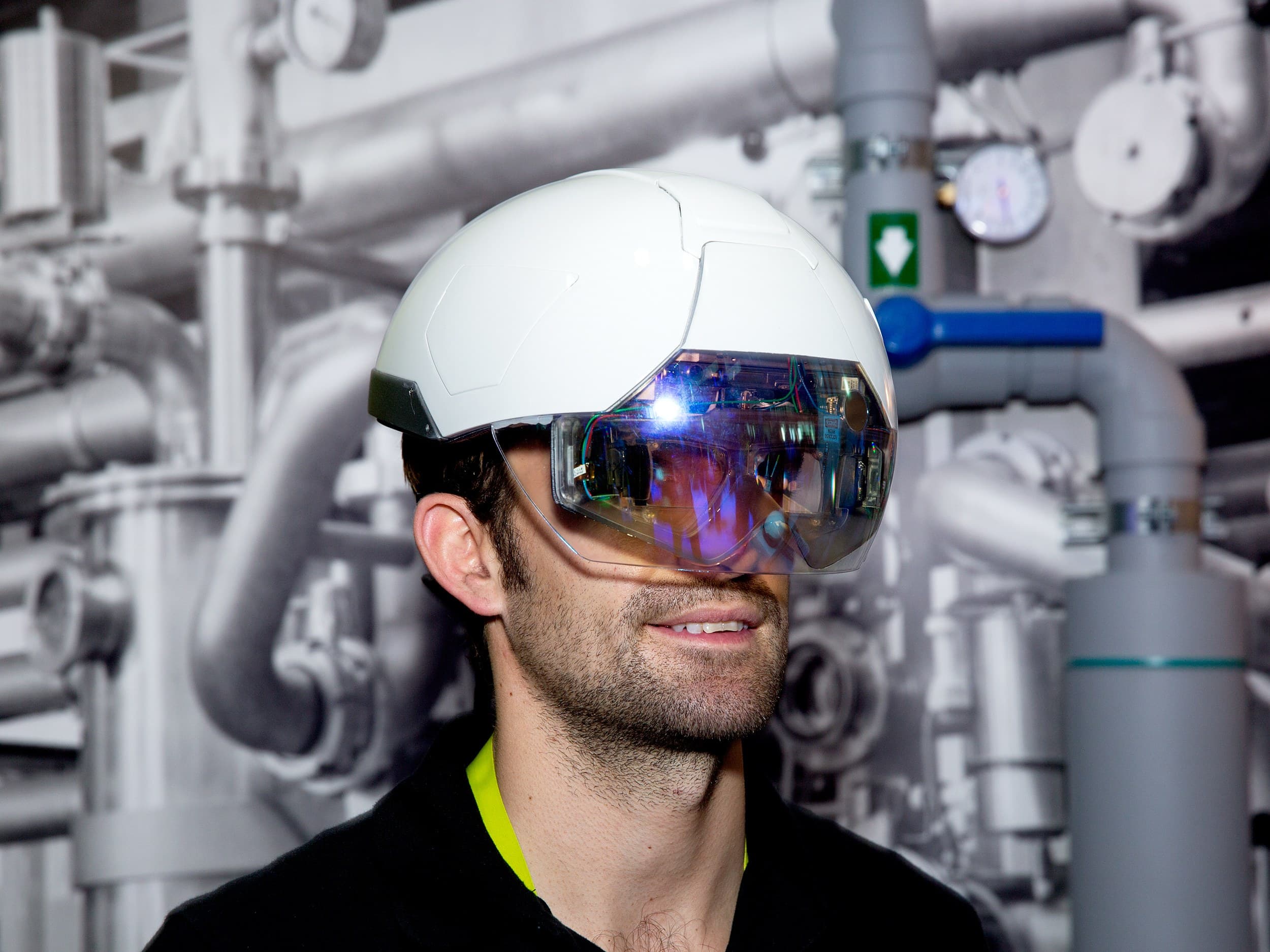

Above: DAQRI's AR smart helmet in action (image courtesy of DAQRI).
The technology provides a digital overlay of our real-world view, offering a range of data to site personnel; from design information to statistics on productivity and health and safety warnings.
3D PRINTING
The use of 3D printing technology is advancing rapidly in the construction sector at all scales.
Accurate digital design information allows 3D printing to be used for everything from rapid prototyping, component manufacture and scale modelling, to the full-scale printing of house and bridge components.
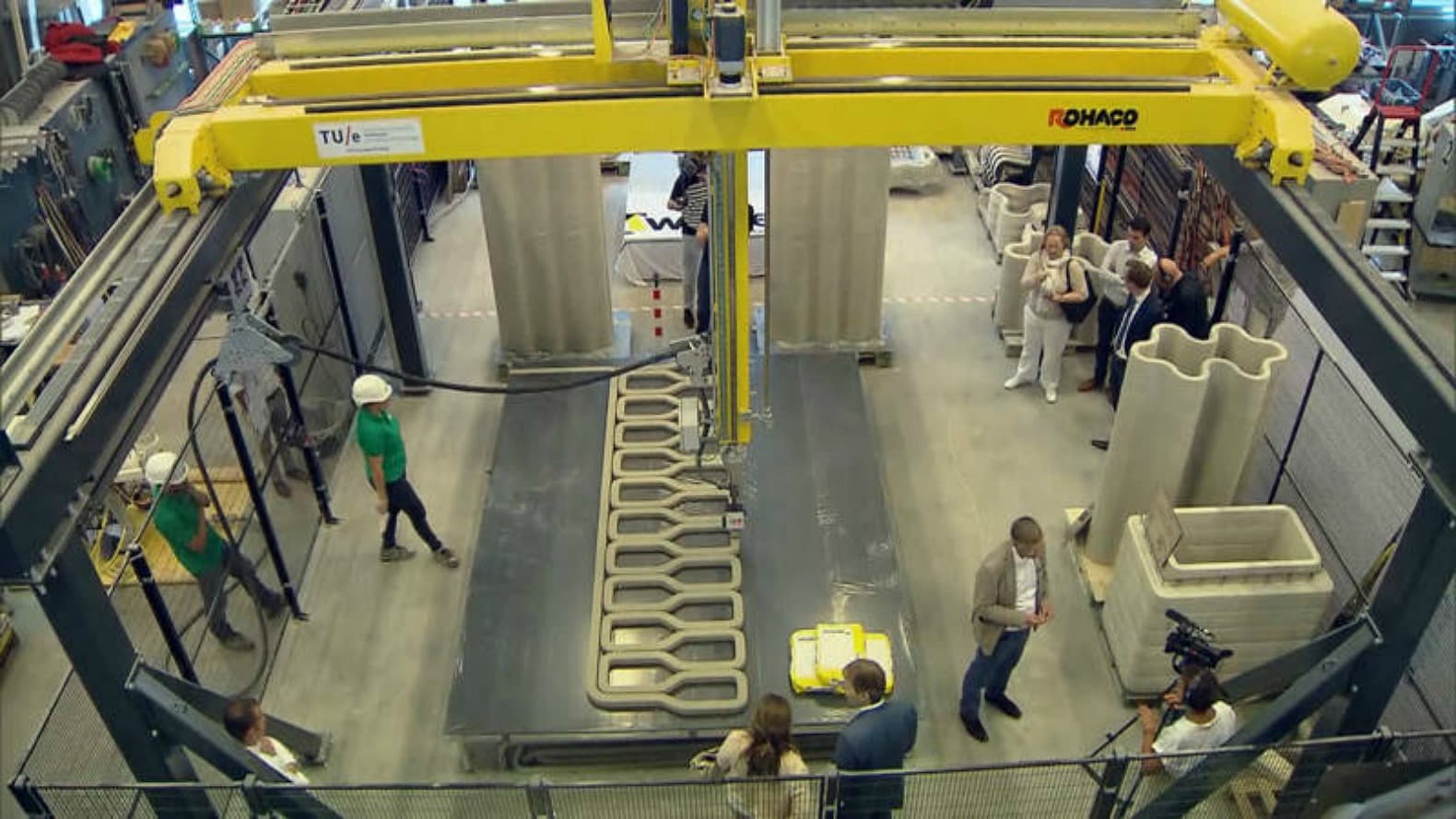

Above: 3D printing has come a long way from the days of small plastic items, the technology is now building entire houses ( image courtesy of Project Milestone)
With a number of prototype structures completing in the past year, countless larger trials proving successful and ambitious plans to 3D print entire housing districts in development, 2019 looks set to be the year that 3D printing moves from the fringes of construction to become a credible structural solution.
THE INTELLIGENT BUILT ENVIRONMENT
The construction industry shapes our world, affects how almost every person on earth is able to live their lives and enables the majority of other businesses and service sectors to operate.
In that context, ensuring that the built environment is operating as effectively as possible is of critical importance to the sustainability and successful development of the human race.

Above: Integrating intelligent systems can help us plan greener and more efficient buildings that better cater to our needs.
By harnessing the data from the digitally enabled built assets we are now creating, our homes, offices and in turn cities can all be operated in a smarter, more efficient, useful and environmentally friendly way.
Furthermore, the data arising can be used to assess trends and to inform the design of future buildings, infrastructure projects and even large-scale city-wide master-plans.
With the effective development of our urban environments on the agenda of countless governments and authorities around the world, we expect to see the importance of this area increase significantly in 2019.
Images and footage courtesy of Hal Robotics, Volvo Construction Equipment,
Odico Formwork Robotics, Doxel, Fastbrick Robotics (FBR), Advanced Construction
Robotics, Japan's National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Boston Dynamics, Graphisoft, Intelligent Buildings, Construction Robotics, Ekso Bionics, Bluebeam, Waymo, Volvo Trucks, PlasticRoad, CarbonCure,
TU Delft, Eelke Dekker, Pavegen, Self Assembly Lab, MIT, Autodesk, Elegant
Embellishments, DAQRI, Multiplex, Freeform, Hewlett Packard, DUS Architects, MX3D, Adriaan De Groot, Joris Laarman, Robert Roozenbeek, Project
Milestone and Viki Knows.
We welcome you sharing our content to inspire others, but please be nice and play by our rules.








